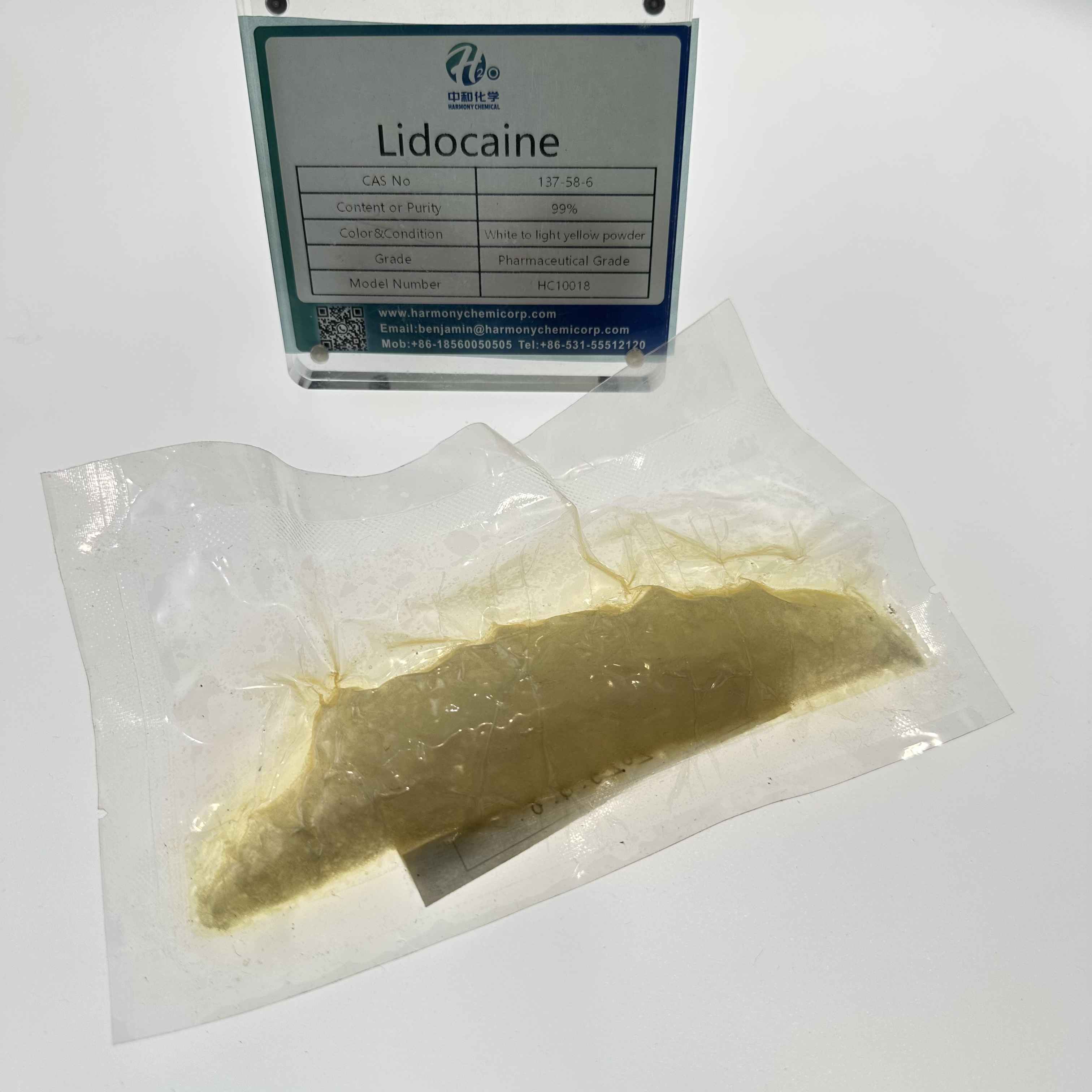
Lidocaine
Lidocaine performs the function of neighborhood anesthesia through reversibly blockading the sodium channel and blockading the transmission of Action attainable on nerve fibers. The Sensory nerve fibers are blocked previously than the Motor nerve fibers, so low dose Lidocaine can play a selective sensory blocking off role. Lidocaine additionally has antiarrhythmic effect, which belongs to Class Ib Antiarrhythmic agent. It can decrease ventricular rate, shorten Action attainable time and absolute refractory period, and extend relative refractory period. Lidocaine has speedy onset and quick duration. Adrenaline introduced to Lidocaine can decrease the charge of systemic absorption, hence prolonging the period of anesthesia.
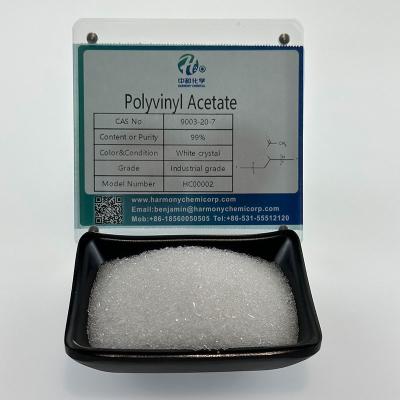
This product is an amide Local anesthetic. Widely used in surface anesthesia, infiltration anesthesia, conduction anesthesia, and epidural anesthesia.

| name | Lidocaine |
| CAS NO | 137-58-6 |
| Molecular formula | C14H22N2O |
| molecular weight | 234.34 |
| melting point | 66-69°C |
| flash point | 9℃ |
| solubility | ethanol: 4 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| colour | White to slightly yellow |
| SOLUBLE | practically insoluble |